Why work with a gut and
microbiome
specialist
during your withdrawal?
POR Addictions Recovery Partnership

Having dysbiosis, or an imbalance in bacterial composition, bacterial metabolic activity or change in bacterial distribution, can make it more challenging to taper off addictive medications. The microbiome’s relevance to neurotransmitter and toxin production cannot be overstated and this is why the Gut is called The Second Brain. Tapering while your gut is imbalanced will exacerbate symptoms for those prone to dysregulated neurotransmitter production, toxin production and processing due to an imbalanced microbiome.
You are welcome to schedule either a brief Free Consultation (clarity call) or Schedule a full Initial Consultation. If you would prefer ongoing support please choose one of our packages.
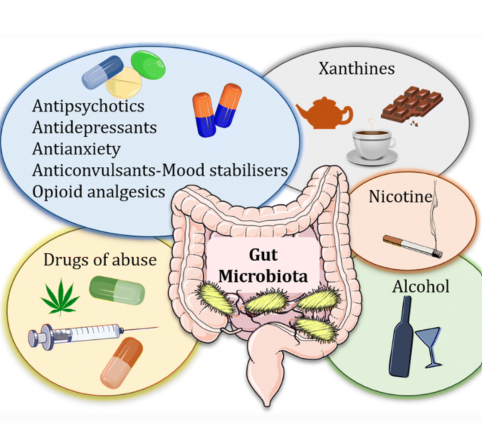
Point of Return helps people throughout the world dependent on Benzodiazepines, Sleeping Pills and Antidepressants. Each classification alters natural gut function, disrupting the healthy microbiome. Benzodiazepines, for example, slow down gut transit time and can predispose one to constipation, candida, infections (such as SIBO and h pylori) and unhealthy microbial overgrowth. Any imbalance increases symptoms, making it more challenging to taper. Healing the gut is critical to a more comfortable taper and overall health.
The addictive medications that POR helps you taper from come with gut function and microbiome altering side effects. Benzodiazepines, for example, slow down gut transit time and can predispose one to constipation and microbial overgrowth.
SSRI’s can increase the presence of serotonin in the gut, which speeds up transit time, making it more difficult for good microbes to maintain their colonies, and making it so that you lose key nutrients.
The stress of tapering alone can create changes in the microbiome, as our gut is filled with stress hormone receptors. Some microbes even use certain stress hormones as fuel.
SSRIs, anti-anxiety medications, NMDA blockers, MAO inhibitors can have antimicrobial effects on the microbiome. Reducing microbes that are important for regulating blood sugar and satiety.